Head and Neck Cancer
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that originate in the various tissues and organs in the head and neck region.
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of cancers that originate in the various tissues and organs in the head and neck region. This includes cancers of the mouth, throat, larynx (voice box), nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, salivary glands, and other areas. These cancers can be aggressive and require careful management.
Common Types of Head and Neck Cancer:
- Oral Cavity Cancer: Includes cancers of the lips, tongue, gums, and other parts of the mouth.
- Pharyngeal Cancer: Affects the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and hypopharynx.
- Laryngeal Cancer: Originates in the larynx (voice box).
- Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinus Cancer: Develops in the nasal cavity or the air-filled spaces around the nose.
- Salivary Gland Cancer: Involves the major and minor salivary glands.
Risk Factors:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco is a significant risk factor for head and neck cancers.
- Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol use, especially when combined with smoking, increases risk.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection: Linked to oropharyngeal cancers.
- Other Factors: Age, gender (more common in males), and exposure to certain chemicals or radiation.
Symptoms:
- Persistent sore throat, hoarseness, or voice changes
- Difficulty swallowing or chewing
- A lump or sore that does not heal
- Nasal obstruction or frequent nosebleeds
- Changes in hearing or vision
Diagnosis:
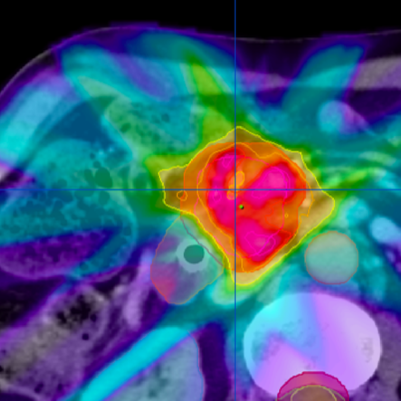
- Imaging: CT, MRI, or PET scans help determine the location and extent of the cancer.
- Biopsy: Tissue samples are examined for cancer cells.
- Endoscopy: Allows for direct visualization of the tumor.
Treatment Options:
- Surgery: Removes the tumor and, in some cases, nearby lymph nodes.
- Radiation Therapy: May be used as a primary treatment or after surgery to target remaining cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Often combined with radiation therapy to increase effectiveness.
- Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs that target specific aspects of cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer cells.
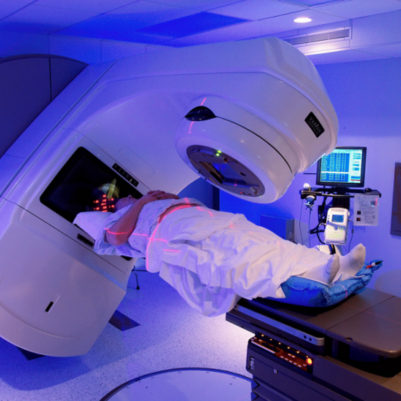
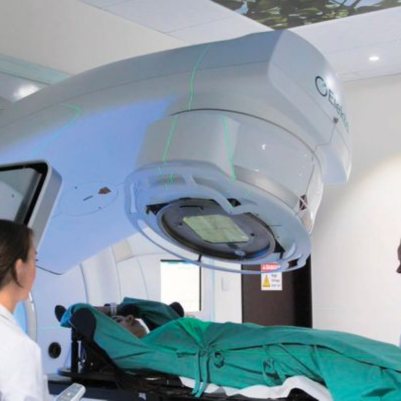
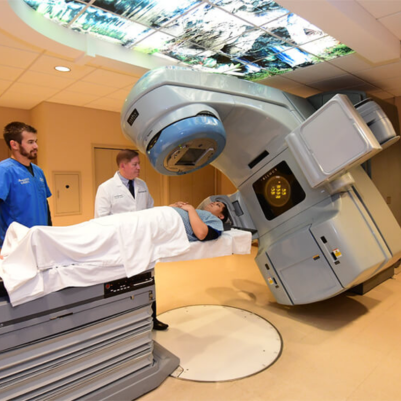
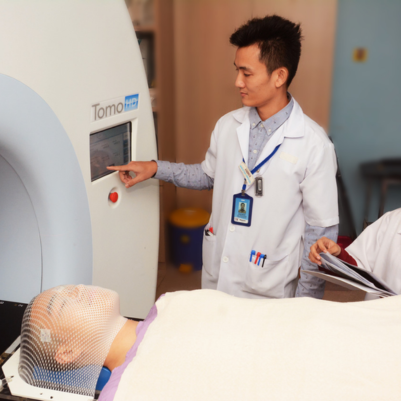
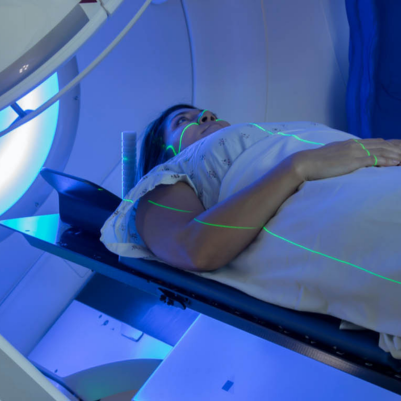
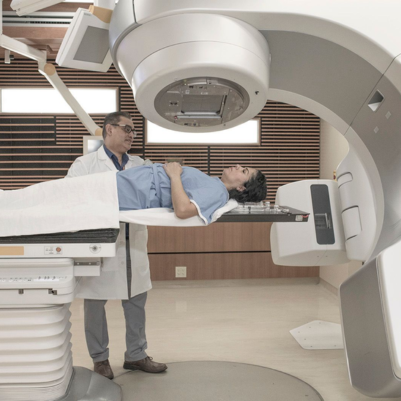
Radiation Therapy in Head and Neck Cancer:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Commonly used to treat head and neck cancer.
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT): Delivers precise radiation doses while sparing healthy tissue.
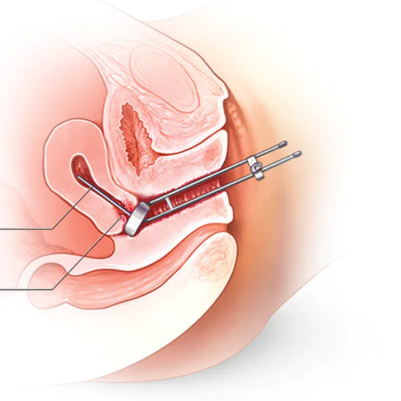
- Brachytherapy: May be used for certain types of head and neck cancer, delivering radiation directly to the tumor.
Support and Rehabilitation:
- Speech and Swallowing Therapy: Helps patients recover or maintain their ability to speak and swallow.
- Nutritional Support: Ensures patients maintain adequate nutrition during treatment.
- Psychological Support: Offers counseling and support for patients and their families.
Conclusion:
Head and neck cancers are complex and can impact essential functions such as speech and swallowing. Early detection and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment are critical for improving outcomes. Treatment plans are individualized based on the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health.