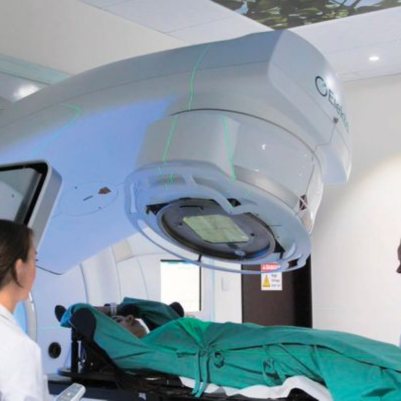
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy
VMAT stands for Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy. It is a type of advanced radiation therapy that combines the precision of Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) with the efficiency of delivering radiation in a continuous arc.
VMAT stands for Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy. It is a type of advanced radiation therapy that combines the precision of Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) with the efficiency of delivering radiation in a continuous arc. VMAT is also known as RapidArc or arc therapy. It allows for precise and efficient radiation delivery while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
Here's an overview of VMAT and its key aspects:
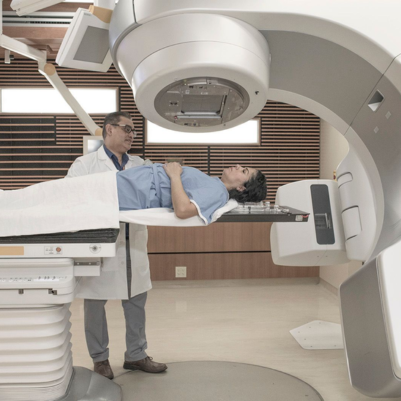
1. Treatment Planning: Like IMRT, VMAT starts with detailed treatment planning using imaging scans such as CT, MRI, or PET scans to accurately identify the tumor and nearby organs at risk. The treatment plan includes the shape and intensity of the radiation beams to optimize the dose to the tumor.
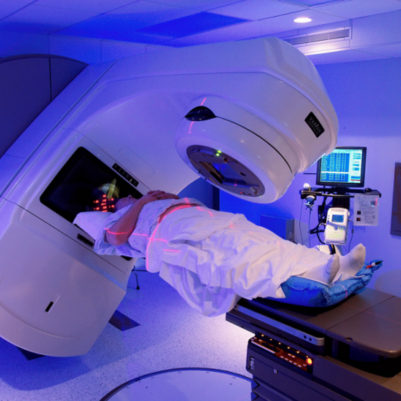
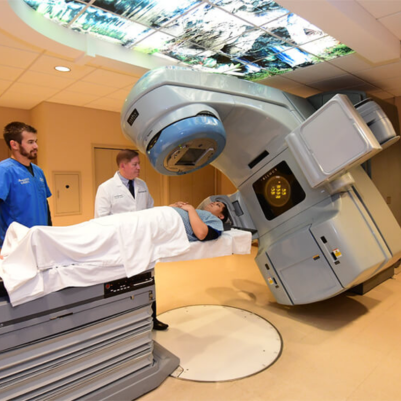
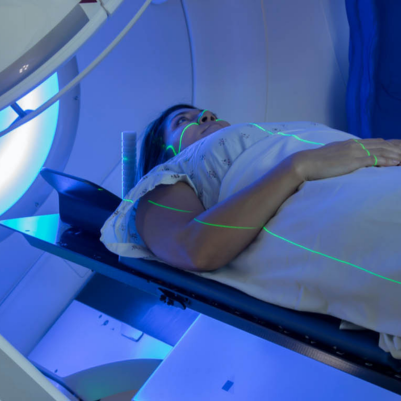
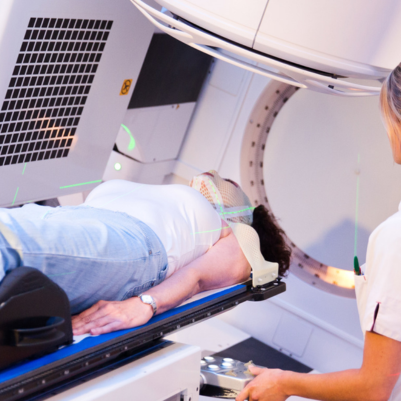
2. Continuous Arc Delivery: VMAT delivers radiation in one or more continuous arcs around the patient. This differs from traditional radiation therapy and IMRT, which deliver radiation from fixed angles. The continuous arc allows for more efficient and uniform dose delivery.
3. Beam Modulation: During treatment, the linear accelerator (linac) modulates the intensity of the radiation beams as it rotates around the patient. Dynamic multileaf collimators (MLCs) shape and modulate the beams to match the tumor's shape.
4. Delivery Speed: One of the main advantages of VMAT is its efficiency. Because the radiation is delivered in a continuous arc, treatment times are generally shorter than with other types of radiation therapy.
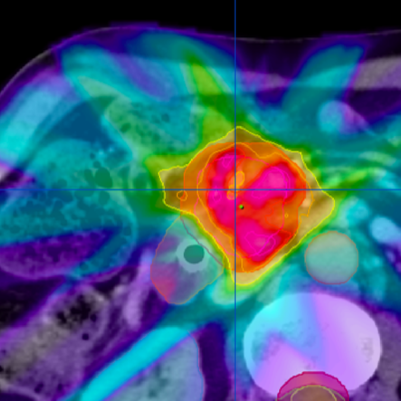
5. Dose Optimization: VMAT uses sophisticated algorithms to optimize the radiation dose delivered to the tumor while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues. This helps achieve high tumor control rates with reduced side effects.
6. Advantages: VMAT offers several advantages, including high precision, efficient delivery, and the ability to treat complex tumors that are located near sensitive structures. The continuous arc delivery also allows for a more even dose distribution.
7. Applications: VMAT can be used to treat a variety of cancers, including cancers of the prostate, lung, head and neck, brain, breast, and gastrointestinal tract. It is particularly useful for treating large or irregularly shaped tumors.
8. Side Effects: VMAT can reduce the risk of side effects compared to conventional radiation therapy. However, side effects may still occur depending on the treatment area and total dose of radiation. Common side effects include skin irritation, fatigue, and localized discomfort.
VMAT is a highly advanced form of radiation therapy that offers a combination of precision, efficiency, and effectiveness in treating cancer. It is often chosen for its ability to deliver high-quality treatment in shorter sessions.