Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT)
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) are advanced radiation therapy techniques used to treat various types of tumors and other medical conditions in the brain and other parts of the body.
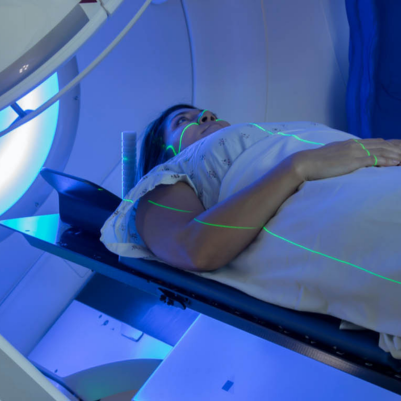
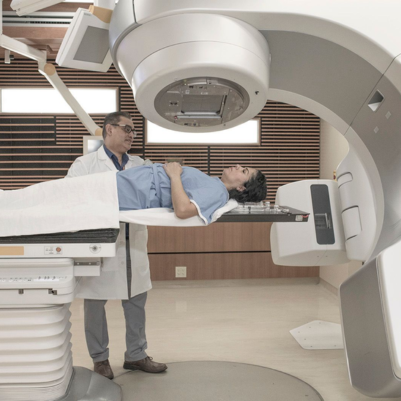
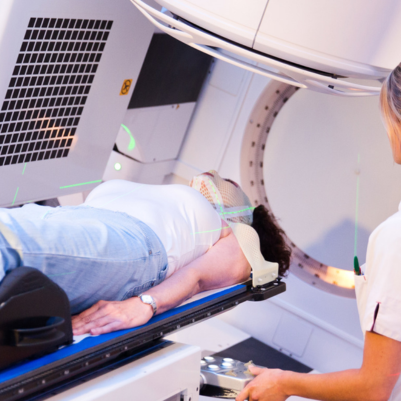
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) are advanced radiation therapy techniques used to treat various types of tumors and other medical conditions in the brain and other parts of the body. Despite the name "surgery," these are non-invasive or minimally invasive methods that use focused, high-dose radiation beams to target specific areas with precision.
Key Features of SRS/SRT:
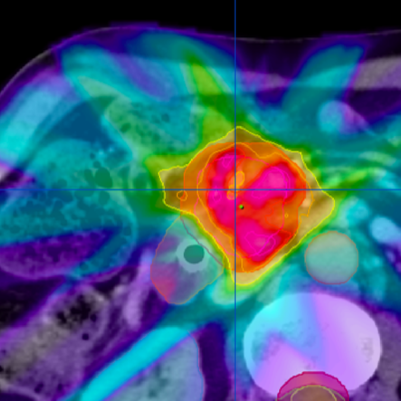
- Precision Targeting: Both SRS and SRT focus high-dose radiation on a specific target, such as a tumor, with millimeter-level precision, sparing surrounding healthy tissue.
- Non-Invasive: These treatments do not require surgical incisions, reducing risks and recovery time for the patient.
- Advanced Imaging: Both techniques use advanced imaging technologies such as MRI, CT, or PET scans to guide the delivery of radiation and ensure accuracy.
- High Dose Delivery: The radiation dose is much higher than in traditional radiation therapy, allowing effective treatment in fewer sessions.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS):
-Single Session: SRS typically involves a single, high-dose radiation treatment session.
- Applications: SRS is commonly used to treat small tumors or lesions in the brain, such as arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), acoustic neuromas, and trigeminal neuralgia. It can also be used for certain types of brain metastases.
Stereotactic Radiotherapy (SRT):
- Multiple Sessions: SRT delivers radiation in smaller doses over multiple sessions, typically a few days.
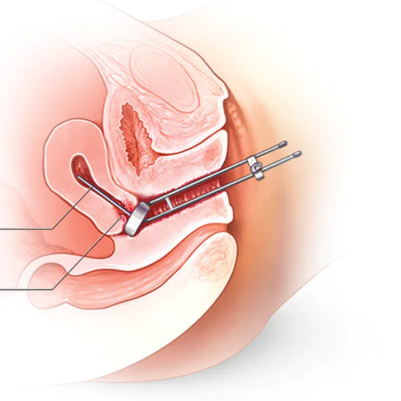
- Applications: SRT is often used for treating larger tumors or lesions in the brain or other areas of the body. It allows for more gradual, controlled treatment.
Benefits of SRS/SRT:
- Minimized Side Effects: The precision targeting helps minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue, reducing side effects.
- Short Treatment Times: Both SRS and SRT offer shorter treatment times compared to conventional radiation therapy.
- Outpatient Procedure: Most patients can receive treatment on an outpatient basis and return home the same day.
- Effective for Various Conditions: These treatments can be used for a range of conditions, including tumors in the brain, lungs, liver, spine, and other parts of the body.
Treatment Planning and Delivery:
- Planning: Planning involves creating a detailed treatment plan using advanced imaging to identify the target area and define the radiation dose and delivery angles.
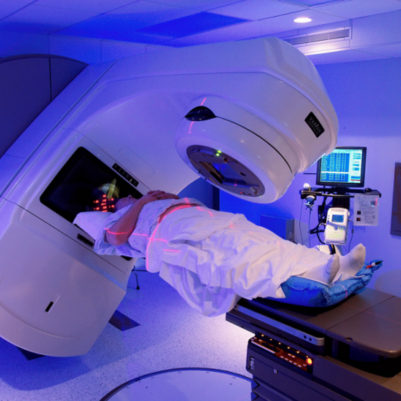
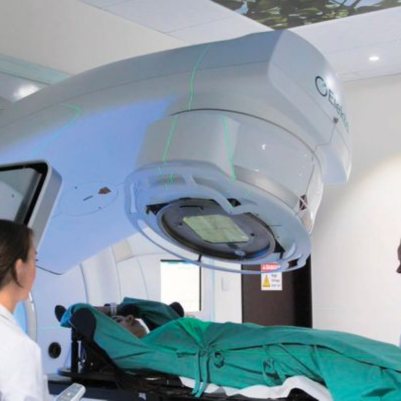
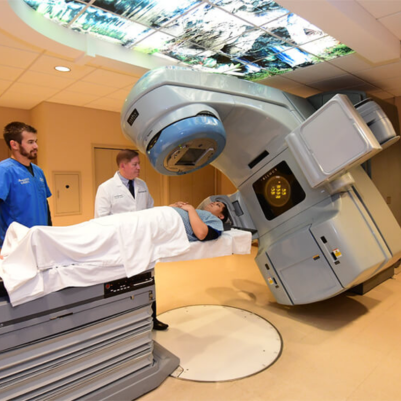
- Delivery: During treatment, the patient is positioned precisely, and radiation is delivered according to the treatment plan using specialized equipment.
Conclusion:
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) are valuable treatments for patients with specific types of tumors or lesions. With their high precision and advanced imaging techniques, they offer effective and efficient options for treating a range of conditions with minimal impact on healthy tissue.